Pioneer log cabins transcend their function as simple shelters, standing as enduring symbols of resilience, self-reliance, and creativity. Built by settlers during the 18th and 19th centuries, these structures embody a time when survival hinged on simplicity and resourcefulness.
From rustic homesteads to frontier outposts, these cabins capture the determination of early settlers who carved homes out of the wilderness. This guide delves into the history, craftsmanship, and legacy of pioneer log cabins, shedding light on the pioneering spirit that shaped their creation.
Table of Contents
The Historical Roots of Pioneer Log Cabins
Traditional Log Construction Techniques
Design and Functionality of Pioneer Log Cabins
Cultural and Symbolic Significance
Modern Interpretations of Pioneer Log Cabins
The Historical Roots of Pioneer Log Cabins
The story of pioneer log cabins in North America dates back to the 1600s, when Swedish and Finnish immigrants introduced traditional log-building methods. These techniques, honed in the forests of Europe, became the foundation for crafting durable and practical homes.
- Colonial Beginnings: The first log structures appeared in the Delaware River Valley. Built from local timber, these homes were valued for their durability and ease of construction.
- Adoption by Settlers: As settlers moved westward, they adapted the log cabin design to meet the demands of frontier life, where isolation and limited resources demanded ingenuity.
- Beyond Shelter: Pioneer cabins served multiple purposes—homes, trading posts, community centers, and even schools.
Fun Fact: Abraham Lincoln, among other notable figures, was born in a log cabin, cementing its symbolic role in the narrative of the “American Dream.”
Traditional Log Construction Techniques
The craftsmanship behind pioneer log cabins reveals a blend of ingenuity and necessity. Builders relied on simple tools and abundant natural materials to construct sturdy, weather-resistant homes.
- Materials and Preparation: Settlers typically used timber like pine, oak, or cedar, valued for its availability and durability. Stripped of bark to prevent decay, the logs were cut to uniform lengths.
- Notching for Stability: Logs were interlocked using notches—such as saddle or dovetail joints—to ensure structural integrity without nails.
- Chinking for Insulation: To seal gaps, builders used mud, moss, or clay, providing insulation against wind and rain.
Design and Functionality
Although humble in appearance, pioneer log cabins were designed with practicality in mind. Every feature had a purpose, reflecting the resourcefulness of their builders.
- Single-Room Layouts: Most cabins consisted of one multifunctional room, housing a kitchen, living area, and sleeping space, centered around a fireplace for warmth and cooking.
- Sleeping Lofts: Often, cabins included lofts for additional sleeping or storage space.
- Minimal Windows and Dirt Floors: Small windows, sometimes covered with oiled paper, provided light while retaining warmth, and floors ranged from packed dirt to wooden planks.
Cultural and Symbolic Significance
Pioneer log cabins hold a special place in American history, representing the perseverance and ingenuity of early settlers.
- Icons of the Frontier: These cabins symbolize self-reliance and the courage to thrive in isolation.
- Humble Beginnings: They embody the ideals of hard work and determination, often associated with figures like Abraham Lincoln.
- Romanticized in Culture: Pioneer cabins are celebrated in literature and folklore as quaint, cozy representations of simpler times.
Historical Note: William Henry Harrison’s 1840 presidential campaign famously used the log cabin as a symbol of his connection to the common man.
Legacy and Preservation
Today, many original log cabins are preserved as historical landmarks, providing a glimpse into the lives of early settlers.
- Restoration Efforts: Museums and heritage sites work to maintain these structures, safeguarding their stories for future generations.
- Inspiring Modern Designs: The timeless appeal of log cabins continues to influence contemporary architecture, blending rustic charm with modern comfort.
Modern Interpretations of Pioneer Log Cabins
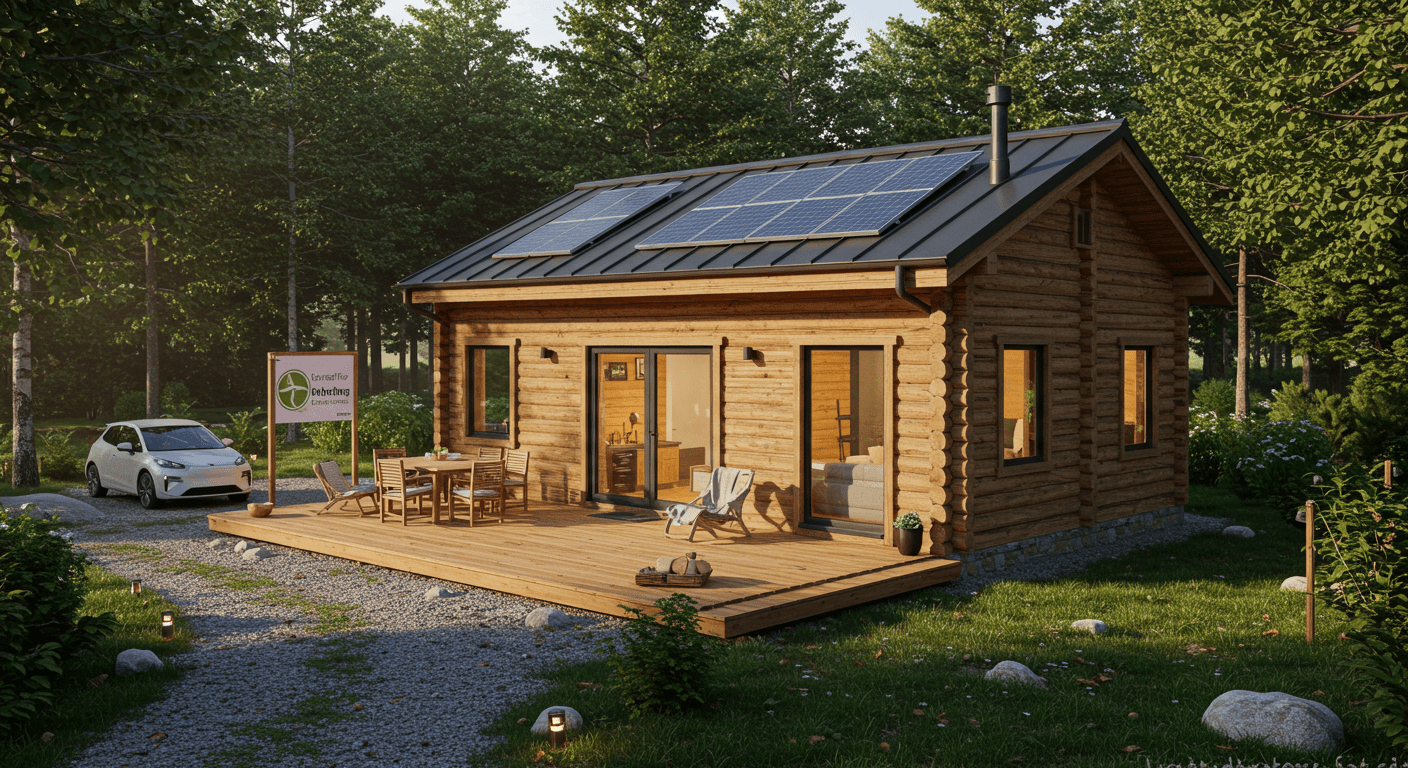
Modern versions of log cabins blend nostalgia with innovation, offering sustainable, luxurious, and versatile living options.
- Prefabricated Cabin Kits: These kits simplify construction, offering customizable designs that reflect traditional aesthetics while incorporating durable, energy-efficient materials.
- Sustainable Living: Off-grid cabins now feature solar panels, rainwater harvesting systems, and modern insulation, making them ideal for eco-friendly lifestyles.
- Vacation Retreats: Log cabins have become popular vacation rentals, combining rustic charm with amenities like Wi-Fi and smart home technology.
Why Pioneer Log Cabins Endure
The lasting appeal of pioneer log cabins lies in their simplicity, practicality, and deep connection to nature.
- Timeless Craftsmanship: The interlocking log construction method remains a durable, sustainable building technique.
- Cultural Heritage: These cabins connect us to a bygone era, offering insights into the resilience and creativity of early settlers.
- Balance of Simplicity and Comfort: Whether serving as homes, vacation getaways, or historical sites, log cabins continue to captivate with their rustic charm.
Conclusion
Pioneer log cabins stand as enduring monuments to the ingenuity and determination of early settlers. Crafted from natural materials, these homes reflect the pioneering spirit of self-reliance and harmony with nature. Whether preserved as historical landmarks or reimagined as modern retreats, log cabins offer lessons in sustainability and simplicity while serving as symbols of resilience and creativity. By cherishing and adapting these timeless structures, we honor the legacy of the pioneers and their remarkable connection to the natural world.